
Mechanical Engineering MEng (Hons)
Mechanical engineers design, create and analyse moving things, solving 21st century problems and shaping the next generation of technology.

Elsewhere on Ulster


Mechanical engineers design, create and analyse moving things, solving 21st century problems and shaping the next generation of technology.
Mechanical engineers create, design and manufacture all kinds of products and processes across a wide range of industries. From automotive to medical devices, aerospace to renewable energy, or materials processing to mobile phones, mechanical engineers are involved at all stages of the product life cycle.
This MEng course will prepare you for a career that is both challenging and rewarding. There is an emphasis on individual and team projects, giving you the opportunity for hands-on involvement and an understanding of engineering materials, processes, devices and systems. Analytical and communication skills are developed with an emphasis on computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacture (CAM). The skills and knowledge acquired are applied to a wide range of real-life engineering problems.
Through a wide range of learning experiences you will develop the intellectual, technical and professional skills that are needed to address 21st century challenges in industry and society. Themes of Design, Mechanical Systems, Materials and Manufacturing run through the course and are further developed through group and individual project work, practical and computer labs, and a range of specialist research-led modules, preparing you for both your industrial placement year and your future career.
We know that choosing to study at university is a big decision, and you may not always be able to find the information you need online.
Please contact Ulster University with any queries or questions you might have about:
For any queries regarding getting help with your application, please select Admissions in the drop down below.
For queries related to course content, including modules and placements, please select Course specific information.
We look forward to hearing from you.
**This course is currently in the process of renewing its Professional Body Accreditation. It is possible that there will be some changes to the course as described.**
This course has been designed with the aid of industrialists to address the needs of industry and the research community. The MEng and BEng Hons Mechanical Engineering courses are taught and assessed in common over the first two years. The third year of each programme is spent on Placement – and successful completion of the Placement year leads to a Diploma in Professional Practice (DPP) which is awarded at Graduation. The BEng Hons students have one additional year of study whereas the MEng students have two additional years of study.
Diploma in Professional Practice DPP
Diploma in Professional Practice International DPPI
Diploma in International Academic Studies DIAS
Typically 18 – 20 hours per week class contact time between 9.15 am and 6.05 pm. There are no timetabled activities on Wednesday afternoons.
Programmes employ a broad range of teaching and assessment styles and place an emphasis on practical demonstrations and on interactive learning opportunities including project-based and group-based activities. The course combines traditional lectures, tutorials and laboratory based classes with technology facilitated resources and activities.
The programme uses a wide range of assessment methods including formal examinations, seen and unseen problems in class tests, on-line multiple-choice assessments, laboratory reports, projects, poster sessions, oral presentations, and peer assessment, where group project work is involved.
The content for each course is summarised on the relevant course page, along with an overview of the modules that make up the course.
Each course is approved by the University and meets the expectations of:

As part of your course induction, you will be provided with details of the organisation and management of the course, including attendance and assessment requirements - usually in the form of a timetable. For full-time courses, the precise timetable for each semester is not confirmed until close to the start date and may be subject to some change in the early weeks as all courses settle into their planned patterns. For part-time courses which require attendance on particular days and times, an expectation of the days and periods of attendance will be included in the letter of offer. A course handbook is also made available.
Courses comprise modules for which the notional effort involved is indicated by its credit rating. Each credit point represents 10 hours of student effort. Undergraduate courses typically contain 10, 20, or 40 credit modules (more usually 20) and postgraduate courses typically 15 or 30 credit modules.
The normal study load expectation for an undergraduate full-time course of study in the standard academic year is 120 credit points. This amounts to around 36-42 hours of expected teaching and learning per week, inclusive of attendance requirements for lectures, seminars, tutorials, practical work, fieldwork or other scheduled classes, private study, and assessment. Teaching and learning activities will be in-person and/or online depending on the nature of the course. Part-time study load is the same as full-time pro-rata, with each credit point representing 10 hours of student effort.
Postgraduate Master’s courses typically comprise 180 credits, taken in three semesters when studied full-time. A Postgraduate Certificate (PGCert) comprises 60 credits and can usually be completed on a part-time basis in one year. A 120-credit Postgraduate Diploma (PGDip) can usually be completed on a part-time basis in two years.
Class contact times vary by course and type of module. Typically, for a module predominantly delivered through lectures you can expect at least 3 contact hours per week (lectures/seminars/tutorials). Laboratory classes often require a greater intensity of attendance in blocks. Some modules may combine lecture and laboratory. The precise model will depend on the course you apply for and may be subject to change from year to year for quality or enhancement reasons. Prospective students will be consulted about any significant changes.

Assessment methods vary and are defined explicitly in each module. Assessment can be a combination of examination and coursework but may also be only one of these methods. Assessment is designed to assess your achievement of the module’s stated learning outcomes. You can expect to receive timely feedback on all coursework assessments. This feedback may be issued individually and/or issued to the group and you will be encouraged to act on this feedback for your own development.
Coursework can take many forms, for example: essay, report, seminar paper, test, presentation, dissertation, design, artefacts, portfolio, journal, group work. The precise form and combination of assessment will depend on the course you apply for and the module. Details will be made available in advance through induction, the course handbook, the module specification, the assessment timetable and the assessment brief. The details are subject to change from year to year for quality or enhancement reasons. You will be consulted about any significant changes.
Normally, a module will have 4 learning outcomes, and no more than 2 items of assessment. An item of assessment can comprise more than one task. The notional workload and the equivalence across types of assessment is standardised. The module pass mark for undergraduate courses is 40%. The module pass mark for postgraduate courses is 50%.

The class of Honours awarded in Bachelor’s degrees is usually determined by calculation of an aggregate mark based on performance across the modules at Levels 5 and 6, (which correspond to the second and third year of full-time attendance).
Level 6 modules contribute 70% of the aggregate mark and Level 5 contributes 30% to the calculation of the class of the award. Classification of integrated Master’s degrees with Honours include a Level 7 component. The calculation in this case is: 50% Level 7, 30% Level 6, 20% Level 5. At least half the Level 5 modules must be studied at the University for Level 5 to be included in the calculation of the class.
All other qualifications have an overall grade determined by results in modules from the final level of study.
In Masters degrees of more than 200 credit points the final 120 points usually determine the overall grading.
Figures from the academic year 2022-2023.
The University employs over 1,000 suitably qualified and experienced academic staff - 60% have PhDs in their subject field and many have professional body recognition.
Courses are taught by staff who are Professors (19%), Readers, Senior Lecturers (22%) or Lecturers (57%).
We require most academic staff to be qualified to teach in higher education: 82% hold either Postgraduate Certificates in Higher Education Practice or higher. Most academic and learning support staff (85%) are recognised as fellows of the Higher Education Academy (HEA) by Advance HE - the university sector professional body for teaching and learning. Many academic and technical staff hold other professional body designations related to their subject or scholarly practice.
The profiles of many academic staff can be found on the University’s departmental websites and give a detailed insight into the range of staffing and expertise. The precise staffing for a course will depend on the department(s) involved and the availability and management of staff. This is subject to change annually and is confirmed in the timetable issued at the start of the course.
Occasionally, teaching may be supplemented by suitably qualified part-time staff (usually qualified researchers) and specialist guest lecturers. In these cases, all staff are inducted, mostly through our staff development programme ‘First Steps to Teaching’. In some cases, usually for provision in one of our out-centres, Recognised University Teachers are involved, supported by the University in suitable professional development for teaching.
Figures from the academic year 2022-2023.
High quality apartment living in Belfast city centre adjacent to the university campus.
Find out more - information about accommodation (Opens in a new window)
At Student Wellbeing we provide many services to help students through their time at Ulster University.
Find out more - information about student wellbeing (Opens in a new window)
Here is a guide to the subjects studied on this course.
Courses are continually reviewed to take advantage of new teaching approaches and developments in research, industry and the professions. Please be aware that modules may change for your year of entry. The exact modules available and their order may vary depending on course updates, staff availability, timetabling and student demand. Please contact the course team for the most up to date module list.
Year: 1
Status: C
This module provides an understanding of the language and terminology of mathematics, together with the mathematical techniques from algebra, calculus and statistics that are necessary for the description and analysis of engineering systems.
Year: 1
Status: C
This module provides an introduction to the fundamentals in the use of a modern 3D CAD system to create robust 3D part modules using an introductory range of feature types. This module provides an introduction to product design specification, design, build and analysis/testing of a product as part of a design project, working as part of a team.
Year: 1
Status: C
Analysis of statics and dynamics systems are a key foundation for mechanical and mechatronic engineers. This module provides fundamental concepts and principles in order to solve static and dynamics problems, and gives a solid methodology and framework in order to tackle new and unfamiliar problems.
Its content includes: Basic and derived units, static equilibrium, statically stressed systems, theory of torsion and bending, kinematics of a particle and kinetics of a particle. Those theoretical and practical principles required within each topic area will be developed in lectures and applied in assignments and tutorials.
Year: 1
Status: C
This module will introduce students to working in multidisciplinary teams to solve a real-world problem and present their solution to an audience of their tutors and peers.
Year: 1
Status: C
A module which integrates lectures with practical sessions in the study of the basics of common manufacturing methodologies and the behaviour of engineering materials. The student will consolidate their learning of the interaction among materials, manufacturing methods, quality and workshop safety. Production of a working electro-mechanical product will deepen knowledge and develop basic skills for selected manufacturing processes. Candidates will critique their work to improve the product design and select appropriate production processes for batch manufacture.
Year: 1
Status: C
This module will introduce students to studying an Engineering Programme at Ulster University and will develop some of the foundational knowledge and skills that will enable them to succeed on their degree programme.
Year: 2
Status: C
The understanding of electrical power systems, AC and DC motors including selection, performance and analysis; plus their relevance to mechanical drive systems.
Year: 2
Status: C
This module provides an introduction to the principles behind fluid mechanics and thermodynamics. Emphasis is placed on the application of this theory to everyday items and to renewable and low-Carbon energy sources and technologies, ranging from relatively simple devices such as pumps, pipes, bicycles, refrigerators and heating systems through to internal combustion engines, hydroelectric power stations and gas turbines
An understanding of how fluids flow, and the forces that result, along with knowledge of energy and how it can be transformed and made more useful are the intended outcomes of this module. It will enable students to continue their study of thermal fluid sciences at a higher level if desired.
Year: 2
Status: C
The module emphasises creativity in design, product innovation, and both technical and non-technical aspects of design. It covers design analysis techniques aimed at achieving sustainable and innovative solutions. The module includes advanced solid modelling tools, assembly modelling, and the creation of 2D drawings. Students will apply these tools and knowledge within a team-based design project.
Year: 2
Status: C
The module uses hybrid learning to provide a sound understanding of the underpinning chemistry and microstructure of metals, ceramics, polymers and composites. How materials properties are controlled by processing techniques, and the role of the engineer in addressing the environmental impact of materials and manufacturing processes are considered. In addition, a programme of industrial visits exposes students to a variety of operations management and production scenarios, permitting insight into commercial manufacturing processes.
Year: 2
Status: C
The module teaches the basics of Operations and Quality. The Operations elements looks at the processes that produce the goods and services sold by the company in addition to optimising facility location and layout. The module also teaches topics such as stock control and scheduling.
The Quality part of the module covers the relevance and application of Quality principles and techniques to the manufacturing environment. Discussion of current topics in Quality Management and Quality Improvement is supported by study of the fundamentals of ISO 9001, Statistical Process Control, Measurement System Analysis and Non-Destructive testing. This module prepares the student to contribute to these challenging activities in their early employment.
Year: 2
Status: C
This module provides an extension of the fundamental principles of Dynamics and Statics/Strength of Materials in relation to mechanical engineering and provides a methodology for their practical application.
Status: O
Year: 3
This module is optional
This module provides undergraduate students with an opportunity to gain structured and professional work experience, in a work-based learning environment, as part of their planned programme of study. This experience allows students to develop, refine and reflect on their key personal and professional skills. The placement should significantly support the development of the student's employability skills, preparation for final year and enhance their employability journey.
Status: O
Year: 3
This module is optional
This module provides an opportunity to undertake an extended period of study outside the UK and Republic of Ireland. Students will develop an enhanced understanding of the academic discipline whilst generating educational and cultural networks.
Year: 4
Status: C
This module provides an understanding of the theoretical concepts and use of feedback-control systems in mechanical engineering.
Year: 4
Status: C
This module is based on the execution of an industrially generated major design project through multi-disciplinary team activity involving aspects of: project management, market analysis, specification, concept design, budget costing, decision making, detail design, production planning, sustainable manufacturing requirements and product costing.
Year: 4
Status: C
This course provides students with an understanding of how solid engineering respond to different types of loading factors. For this, theoretical and practical principles required in static, dynamic and FEA disciplines will be taught in lectures and applied in assignments, laboratory sessions and tutorials. These will allow students to assess and deliver a solution for a variety of practical mechanical systems.
Year: 4
Status: C
This introductory module is to equip students with a basic linguistic competence and give them confidence in their own language learning abilities. The teaching methods aim at encouraging learner autonomy at the crucial early stages of language acquisition. The research on aspects of contemporary German society is to tune the students' sensitivity to another culture
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module provides students with a detailed understanding of the composition, function and application of synthetic and natural biomaterials in the context of the medical implant devices they are used to fabricate. The approach taken highlights the important materials science issues involved in the provision of these systems. The increasing importance of functional biomaterials to the provision of enhanced medical implant devices that can more effectively replace damaged and/or diseased tissues and organs is also addressed.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module gives the student an overview of nanotechnology and its applications in engineering.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
The module is offered in Germany and covers theoretical and practical aspects of modern process automation concepts.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module is offered in Germany and covers the theoretical and practical aspects of mechatronics, control and simulation techniques for micro-mechanical systems combined with electronics and bonding technologies to connect both.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
The module is offered in Germany and covers the incentives and decision making processes of different market participants. Students learn to use economic concepts in order to evaluate the consequences of current economic developments for making decisions.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module introduces environmental issues, key aspects and provides coverage of science, technology, design, regulations and management systems pertaining to environmental protection, resource conservation and alternative energy sources.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module covers smart manufacturing technologies aligned with Industry 4.0, including industrial and mobile robotics, robot applications, machine learning and its applications in manufacturing, as well as advanced composite manufacturing techniques.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
The module is offered in Germany and covers theoretical and practical aspects of modern MEMS concepts.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module provides practical, hands-on experience of Computer Aided Engineering in the context of industrial design and manufacturing. It focuses on advanced part modelling techniques, assembly modelling, creating associative links, good modelling practice, collaboration and interoperability, design documentation, 3D printing, surface modelling, photorealistic rendering, dynamic simulation, Finite Element Analysis and virtual reality. It involves the utilisation of an integrated, state-of-the-art MCAD suite, along with the teaching of the general principles of the aforementioned technologies.
Year: 5
Status: C
A module which integrates lectures with group activities in the study of the basics of research methods and management processes. The student will consolidate their learning of research methodologies, management processes, data processing, literature review, report and dissertation writing and presentations.
Year: 5
Status: C
This module is designed to equip students with the research and project management skills necessary to successfully complete an MEng-level project and to prepare them to contribute effectively in their first engineering graduate roles.
An ethos of professionalism is fostered and demonstrated through the application of previously learned material to practical engineering challenges. This commitment to professional standards is essential for ongoing development and is a core requirement of a practising Chartered Engineer.
Students are expected to design their project in collaboration with their supervisor. They will take responsibility for executing the project and for communicating their work through an oral/poster presentation and a final written dissertation.
Year: 5
Status: C
This module in thermal fluid sciences covers external flow, turbulence and heat transfer and a practical introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics modelling using commercial software
Status: O
Year: 5
This module is optional
The course provides an in depth knowledge of micro-nanodevices, as well as micro and nanofabrication techniques using elements from nanoscience and nanotechnology.
Status: O
Year: 5
This module is optional
To provide participants with the capability to improve the competitiveness of companies through entrepreneurship practice and new product and/or process innovation. A major team design project is addressed derived from a real problem from within a local/global manufacturing company. Material covered is supported through tutorial, lecture and workshop sessions as appropriate.
Status: O
Year: 5
This module is optional
Two of the most important developments in manufacturing in the 21st century are Additive Manufacturing and the 4th Industrial Revolution (Industrie 4.0). In this module, students will be introduced to these two strands of advanced manufacturing and will develop the skills and knowledge to engage with these concepts in an industrial context.
Status: O
Year: 5
This module is optional
This module provides a concise review of modern manufacturing, time compression methodologies and current manufacturing systems - their specification, implementation and development. The flow of data within a product lifecycle is analysed from design through to manufacture and the effective utilisation of advanced manufacturing technology addressed.
Status: O
Year: 5
This module is optional
This module considers modern approaches to Quality Improvement. The context of product or service is set for the interpretation of Quality from different perspectives. The Quality topics are considered under the themes of definition, measurement, actions, improvement and control. Modern and traditional management approaches are evaluated and techniques appropriate to product or service characteristics and organisation performance are considered.
Status: O
Year: 5
This module is optional
This module provides a concise and application based overview of current computer aided engineering systems by providing a detailed summary of current rapid-prototyping and manufacturing processes, multi-axis advanced manufacturing technologies, digital inspection and simulation. The application of CAE to enhance the product lifecycle will be the fundamental objective of this module. The integration of these systems from new product introduction (NPI) through to digital inspection will be addressed.
Status: O
Year: 5
This module is optional
At the end of the module the student should be able to critically appraise alternative thermoplastic conversion and fabrication processing routes. Through analysis of processing behaviour, they should be capable of developing appropriate strategy for selection of conversion routes for a range of representative material systems and applications in terms of total economics and quality enhancement.
Status: O
Year: 5
This module is optional
At the end of the module the student should have acquired a high level of competence the many facets of composite materials and their processing methods leading to an active role as a member of a Production Management or Research team. The student should have the ability to select between competing 'composite' technologies for specific applications and hence be in a position to devise conversion systems and associated quality assurance procedures, having regard to maximising cost effectiveness and product reliability.
We recognise a range of qualifications for admission to our courses. In addition to the specific entry conditions for this course you must also meet the University’s General Entrance Requirements.
ABB to include Mathematics and one from Physics, Chemistry, Technology & Design, Engineering or Electronics.
OR
BBC if presenting A Level Physics in addition to Mathematics
NOTE:
Applicants for the MEng Hons Mechanical Engineering course, not eligible for entry to the MEng, will automatically be considered for entry to the BEng Hons Mechanical Engineering course both at offer making stage and once results have been received.
RQF Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Extended Diploma in Engineering with overall award profile DDM to include a Distinction in Engineering Principles and a Distinction in Further Engineering Mathematics.
A Levels with;
RQF Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Extended Certificate combined with A Levels Mathematics and one other specified A Level (please refer to A Level section).
RQF Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Extended Certificate in Engineering will satisfy the subject requirement as long as it includes Distinction in Engineering Principles combined with A Level Mathematics and one other A level.
RQF Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Diploma in Engineering to include Distinction in Engineering Principles and Distinction in Further Engineering Mathematics combined with a specified A Level (please refer to A Level section).
RQF Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Foundation Diploma does not satisfy the subject requirement for this course and will only be considered when presented with A Levels in the specified subjects.
The A level(s) must include Mathematics plus an A Level in a specified subject and/or the BTEC Level 3 qualification(s) must be in the specified subject(s) and must have the required modules.
OCR Nationals and Cambridge Technical Combinations
Do not satisfy the subject entry requirement for this course and will be accepted as grade only when presented with A levels in the relevant subjects.
To find out if the qualification you are applying with is a qualification we accept for entry, please check our Qualification Checker - our Equivalence Entry Checker.
We will also continue to accept QCF versions of these qualifications although grades asked for may differ. Check what grades you will be asked for by comparing the requirements above with the information under QCF in the Applied General and Tech Level Qualifications section of our Entry Requirements - View our Undergraduate Entry Requirements
Entry equivalences can also be viewed in the online prospectus at our Equivalence Entry Checker.
128 UCAS Tariff points to include a minimum of five subjects (four of which must be at Higher Level) to include English at H6 if studied at Higher Level or O4 if studied at Ordinary Level.
Higher Level subjects must include Mathematics at minimum H5 and one other Higher Level subject at minimum Grade H6 from Physics, Chemistry, Physics/Chemistry, Biology, Technology, Engineering, Technology and Design.
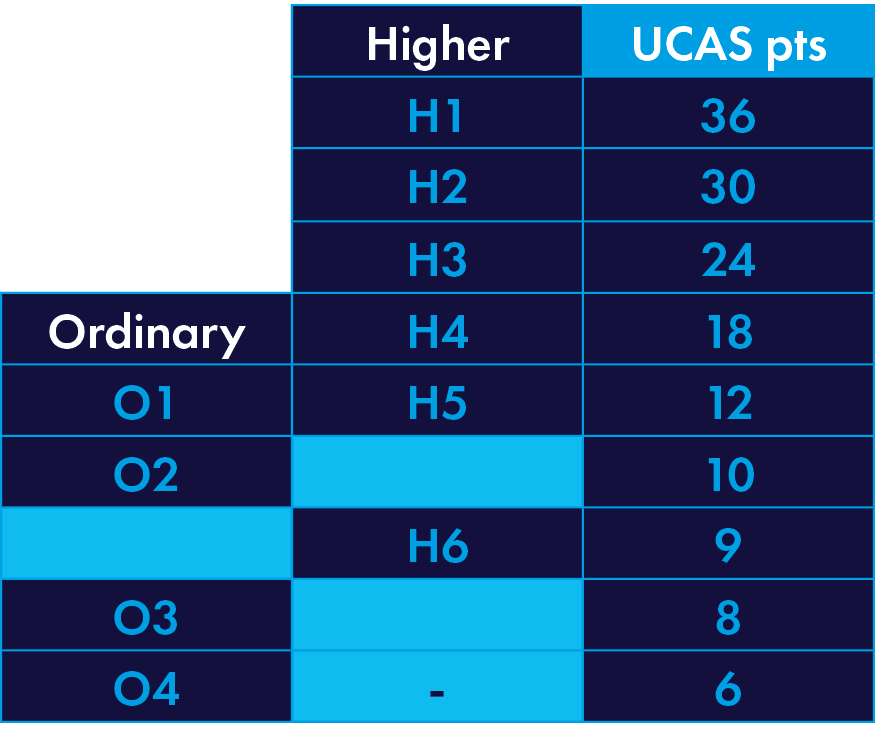
Grades BBBBC (to include minimum of BB in Mathematics and another science subject).
Grades BBC (to include Mathematics and a science subject).
Overall profile is minimum of 27 points to include 13 at Higher Level and to include minimum grade 6 in Higher Level Mathematics and grade 5 in another Higher Level science subject. Grade 4 in English Language also required in overall profile.
MEng entry is not available directly from an Access course.
For full-time study, you must satisfy the General Entrance Requirements for admission to a first degree course and hold a GCSE pass at Grade C/4 or above in English Language.
GCSE pass at Grade C/4 or above in Mathematics (or alternative qualification acceptable to the University).
Level 2 Certificate in Essential Skills - Communication, will be accepted as equivalent to GCSE English.
Please note that for purposes of entry to this course the Level 2 Certificate in Essential Skills - Application of Number is NOT regarded as an acceptable alternative to GCSE Mathematics.
English language requirements for international applicants
The minimum requirement for this course is Academic IELTS 6.0 with no band score less than 5.5. Trinity ISE: Pass at level III also meets this requirement for Tier 4 visa purposes.
Ulster recognises a number of other English language tests and comparable IELTS equivalent scores.
HND, HNC, Foundation and OCR/Cambridge Technical do not satisfy the subject entry requirements to this course.
The General Entry Requirements must also be met including English Language minimum GCSE grade C (or equivalent). Please check the following link General Entry Requirements
If you require a Student Route Visa you will need a valid ATAS Certificate
Students who have successfully completed studies equivalent in content and level to year 1 modules may be considered for direct entry to Year 2.
Graduates from this course are now working for:
With this degree you could become:
Job prospects in a broad range of engineering industries are excellent with most graduates finding employment within six months of graduation. Graduates with an MEng in Mechanical Engineering, first class or upper second class award satisfy the entry requirements for a wide range of postgraduate research posts and scholarships in mechanical engineering, engineering materials and manufacturing engineering.
The industrial placement year is a significant, formative period for our student mechanical engineers. Involvement in the practice of engineering in an industrial setting will develop your engineering, transferable and personal skills and significantly enhance your employability on graduation. All students are therefore required to undertake a (paid) industrial work placement - normally in year 3 of the programme.
In addition, students can select to study for a semester in the University of Applied Sciences in Augsburg which is in the Bavarian region of Germany. This study abroad period is normally in semester 2 of year 4.
Accreditations reflect the excellence of our teaching, research, and knowledge exchange and ensure our programmes realise the highest expectations. By studying at Ulster University you’ll gain insight and be at the forefront of current industry practices, while our many accredited degree programmes open doors to the world’s top professional organisations, making you more attractive to future employers and giving you a competitive edge in the job market.
Accredited by the Institution of Engineering and Technology on behalf of the Engineering Council for the purposes of fully meeting the academic requirement for registration as a Chartered Engineer.
Accredited by the Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMechE) on behalf of the Engineering Council for the purposes of fully meeting the academic requirement for registration as a Chartered Engineer.
Undergraduate fees are subject to annual review, 2026/27 fees will be announced in due course.
See our tuition fees page for the current fees for 2025/26 entry.
It is important to remember that costs associated with accommodation, travel (including car parking charges) and normal living will need to be covered in addition to tuition fees.
Where a course has additional mandatory expenses (in addition to tuition fees) we make every effort to highlight them above. We aim to provide students with the learning materials needed to support their studies. Our libraries are a valuable resource with an extensive collection of books and journals, as well as first-class facilities and IT equipment. Computer suites and free Wi-Fi are also available on each of the campuses.
There are additional fees for examination resits and library fines. Where a graduation ceremony is part of your course, please be aware that additional fees will apply.
Students choosing a period of paid work placement or study abroad as a part of their course should be aware that there may be additional travel and living costs, as well as tuition fees.
See the tuition fees on our student guide for most up to date costs.
Ulster continues to develop and support sustainability initiatives with our staff, students, and external partners across various aspects of teaching, research, professional services operations, and governance.
At Ulster every person, course, research project, and professional service area on every campus either does or can contribute in some way towards the global sustainability and climate change agenda.
We are guided by both our University Strategy People, Place and Partnerships: Delivering Sustainable Futures for All and the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Our work in this area is already being recognised globally. Most recently by the 2024 Times Higher Education Impact rating where we were recognised as Joint 5th Globally for Outreach Activities and Joint Top 20 Globally for Sustainable Development Goal 17: Partnership for the Goals.
Visit our Sustainability at Ulster destination to learn more about how the University strategy and the activities of Ulster University support each of the Sustainable Development Goals.
1. We prepare our prospectus and online information about our courses with care and every effort is made to ensure that the information is accurate. The printed version of the prospectus is, however, published at least a year before the courses begin. Information included in the prospectus may, therefore, change. This includes, but is not limited to changes to the terms, content, delivery, location, method of assessments or lengths of the courses described. Not all circumstances are foreseeable, but changes will normally be made for one of the following reasons:
2. If there are insufficient enrolments to make a course viable, it may be necessary for the University to withdraw a course. If you have received an offer for a course that we subsequently have to close, we will contact you as soon as possible to discuss alternative courses. If you do not wish to study any alternative courses at the University, you may withdraw your application by informing us by email to admissions@ulster.ac.uk.
3. Please note that the University’s website is the most up-to-date source of information regarding courses, campuses and facilities and we strongly recommend that you always visit the website before making any commitments.
4. We will include a durable PDF when we send you an offer letter which will highlight any changes made to our prospectus or online information about our courses. You should read this carefully and ensure you fully understand what you are agreeing to before accepting a place on one of our courses.
5. The University will always try to deliver the course as described in the durable PDF you receive with your offer letter.
6. At any point after an offer has been made, students will be notified of any course changes in writing (usually by email) as soon as reasonably practicable and we will take all reasonable steps to minimise their impact where possible. The University will, where possible and reasonably practicable, seek the express consent of the student in regard to any changes concerning material or pre-contract information.
7. The University website will be updated to reflect the changed course information as soon as reasonably practicable.
8. If, after due consideration, you decide that you no longer want to study your course or to study at the University because of the changes, you may withdraw your application or terminate your contract with the University. In order to do so, you should notify us in writing by emailing admissions@ulster.ac.uk (and update UCAS if applicable). We will, on request, recommend alternative courses that you could study with us, or suggest a suitable course at an alternative higher education provider.
9. If you do not agree that the changes are fair, you can seek redress under the Student Complaints Procedures.
10. Providing the University has complied with the requirements of all applicable consumer protection laws, the University does not accept responsibility for the consequences of any modification, relocation or cancellation of any course, or part of a course, offered by the University. The University will give due and proper consideration to the effects thereof on individual students and take the steps necessary to minimise the impact of such effects on those affected.
11. The University is not liable for disruption to its provision of educational or other services caused by circumstances beyond its reasonable control providing it takes all reasonable steps to minimise the resultant disruption to such services.
12. Further information can be found in our terms and conditions.
The full Student Terms and Conditions is now available.