
Criminology and Criminal Justice BSc (Hons)
Criminology and criminal justice addresses crime, deviance and its control through an applied, interesting and intellectually challenging curriculum.

Elsewhere on Ulster


Criminology and criminal justice addresses crime, deviance and its control through an applied, interesting and intellectually challenging curriculum.
The BSc Hons Criminology and Criminal Justice degree and the Criminology minor degrees aim to provide you with a knowledge of key criminological concepts, theoretical approaches and the necessary knowledge and skills required to undertake criminological research. The course aims to enable you to demonstrate understanding of the criminal justice system and the political, social and economic context within which it operates. You will be supported in developing a professional attitude and a responsibility for individual learning and team work.
We know that choosing to study at university is a big decision, and you may not always be able to find the information you need online.
Please contact Ulster University with any queries or questions you might have about:
For any queries regarding getting help with your application, please select Admissions in the drop down below.
For queries related to course content, including modules and placements, please select Course specific information.
We look forward to hearing from you.
Criminology, as an area of study, has a lengthy pedigree and you will be presented throughout the course with a range of ideas and theories from several different disciplines including law, public policy, social policy and economics. You will study criminological concepts and issues related to criminal justice such as crime and deviance, victims, policing, sentencing and punishment and emergent ideas on state, corporate, and environmental crime. These, coupled with knowledge of institutions and structures, will provide you with a wider understanding of behaviour and activity within the criminal justice system.
The degree will provide you with the opportunity to gain a combination of theoretical knowledge and a range of skills necessary for employment in organisations with a criminal justice focus within the private, voluntary and statutory sectors.
Diploma in Professional Practice DPP
Diploma in International Academic Studies DIAS
Teaching takes place over two 12 week semesters. Contact hours during the teaching weeks are 9 hours a week, supplemented by at least 25 hours of independent study. In final year students have additional dissertation supervision sessions and throughout the course students have access to their studies advisor and year tutor when the need arises. All course team staff are available for individual consultation at set times and by arrangement.
A variety of teaching and learning methods are used on the degree including lectures, seminars, supervised group-work sessions, directed reading, blended learning using Blackboard Learn, case study work, directed electronic information retrieval, independent learning, and a work-based-learning opportunity to impart knowledge and understanding of the subject. In addition, a broad range of assessment methods are utilised to measure knowledge and understanding of the subject, including academic essays; report writing; policy analysis/policy brief-writing; directed seminar discussions, small-group project work; writing and delivering seminar papers; presentations; online tests; the dissertation, e-portfolios, blogs and unseen examinations.
The content for each course is summarised on the relevant course page, along with an overview of the modules that make up the course.
Each course is approved by the University and meets the expectations of:

As part of your course induction, you will be provided with details of the organisation and management of the course, including attendance and assessment requirements - usually in the form of a timetable. For full-time courses, the precise timetable for each semester is not confirmed until close to the start date and may be subject to some change in the early weeks as all courses settle into their planned patterns. For part-time courses which require attendance on particular days and times, an expectation of the days and periods of attendance will be included in the letter of offer. A course handbook is also made available.
Courses comprise modules for which the notional effort involved is indicated by its credit rating. Each credit point represents 10 hours of student effort. Undergraduate courses typically contain 10, 20, or 40 credit modules (more usually 20) and postgraduate courses typically 15 or 30 credit modules.
The normal study load expectation for an undergraduate full-time course of study in the standard academic year is 120 credit points. This amounts to around 36-42 hours of expected teaching and learning per week, inclusive of attendance requirements for lectures, seminars, tutorials, practical work, fieldwork or other scheduled classes, private study, and assessment. Teaching and learning activities will be in-person and/or online depending on the nature of the course. Part-time study load is the same as full-time pro-rata, with each credit point representing 10 hours of student effort.
Postgraduate Master’s courses typically comprise 180 credits, taken in three semesters when studied full-time. A Postgraduate Certificate (PGCert) comprises 60 credits and can usually be completed on a part-time basis in one year. A 120-credit Postgraduate Diploma (PGDip) can usually be completed on a part-time basis in two years.
Class contact times vary by course and type of module. Typically, for a module predominantly delivered through lectures you can expect at least 3 contact hours per week (lectures/seminars/tutorials). Laboratory classes often require a greater intensity of attendance in blocks. Some modules may combine lecture and laboratory. The precise model will depend on the course you apply for and may be subject to change from year to year for quality or enhancement reasons. Prospective students will be consulted about any significant changes.

Assessment methods vary and are defined explicitly in each module. Assessment can be a combination of examination and coursework but may also be only one of these methods. Assessment is designed to assess your achievement of the module’s stated learning outcomes. You can expect to receive timely feedback on all coursework assessments. This feedback may be issued individually and/or issued to the group and you will be encouraged to act on this feedback for your own development.
Coursework can take many forms, for example: essay, report, seminar paper, test, presentation, dissertation, design, artefacts, portfolio, journal, group work. The precise form and combination of assessment will depend on the course you apply for and the module. Details will be made available in advance through induction, the course handbook, the module specification, the assessment timetable and the assessment brief. The details are subject to change from year to year for quality or enhancement reasons. You will be consulted about any significant changes.
Normally, a module will have 4 learning outcomes, and no more than 2 items of assessment. An item of assessment can comprise more than one task. The notional workload and the equivalence across types of assessment is standardised. The module pass mark for undergraduate courses is 40%. The module pass mark for postgraduate courses is 50%.

The class of Honours awarded in Bachelor’s degrees is usually determined by calculation of an aggregate mark based on performance across the modules at Levels 5 and 6, (which correspond to the second and third year of full-time attendance).
Level 6 modules contribute 70% of the aggregate mark and Level 5 contributes 30% to the calculation of the class of the award. Classification of integrated Master’s degrees with Honours include a Level 7 component. The calculation in this case is: 50% Level 7, 30% Level 6, 20% Level 5. At least half the Level 5 modules must be studied at the University for Level 5 to be included in the calculation of the class.
All other qualifications have an overall grade determined by results in modules from the final level of study.
In Masters degrees of more than 200 credit points the final 120 points usually determine the overall grading.
Figures from the academic year 2022-2023.
The University employs over 1,000 suitably qualified and experienced academic staff - 60% have PhDs in their subject field and many have professional body recognition.
Courses are taught by staff who are Professors (19%), Readers, Senior Lecturers (22%) or Lecturers (57%).
We require most academic staff to be qualified to teach in higher education: 82% hold either Postgraduate Certificates in Higher Education Practice or higher. Most academic and learning support staff (85%) are recognised as fellows of the Higher Education Academy (HEA) by Advance HE - the university sector professional body for teaching and learning. Many academic and technical staff hold other professional body designations related to their subject or scholarly practice.
The profiles of many academic staff can be found on the University’s departmental websites and give a detailed insight into the range of staffing and expertise. The precise staffing for a course will depend on the department(s) involved and the availability and management of staff. This is subject to change annually and is confirmed in the timetable issued at the start of the course.
Occasionally, teaching may be supplemented by suitably qualified part-time staff (usually qualified researchers) and specialist guest lecturers. In these cases, all staff are inducted, mostly through our staff development programme ‘First Steps to Teaching’. In some cases, usually for provision in one of our out-centres, Recognised University Teachers are involved, supported by the University in suitable professional development for teaching.
Figures from the academic year 2022-2023.
High quality apartment living in Belfast city centre adjacent to the university campus.
Find out more - information about accommodation (Opens in a new window)
At Student Wellbeing we provide many services to help students through their time at Ulster University.
Find out more - information about student wellbeing (Opens in a new window)
Here is a guide to the subjects studied on this course.
Courses are continually reviewed to take advantage of new teaching approaches and developments in research, industry and the professions. Please be aware that modules may change for your year of entry. The exact modules available and their order may vary depending on course updates, staff availability, timetabling and student demand. Please contact the course team for the most up to date module list.
Year: 1
Status: C
The overall aim of this module is to introduce criminology students to basic legal skills and how to use those effectively. Specifically, the objectives of this module are to teach the sources of law; how to find the law and to use legal materials to present reasoned arguments orally or in writing and to instil an ability to communicate effectively in a variety of forms. The skills and knowledge learnt in this module will be fundamental to all modules studied on the degree programme. Further this module will assist with one of the goals of developing students as independent learners.
Year: 1
Status: C
Crime is an ever-pervasive social problem in contemporary society and forensic science has a role to play in the fight against crime. This module provides students with a basic introduction to forensic science starting with an understanding of what forensic science is, how it has developed over the years, how crime scene and forensic examination are carried out, the principles behind these investigations, the potential value such investigations may have in criminal investigations, courtroom procedures in relation to forensic evidence and the role of the expert witness. The module will also foster the cultivation of the criminal skills needed to evaluate the contribution of forensic science to the criminal justice system and will provide an important foundation of knowledge and skills for the criminology and criminal justice degree.
Year: 1
Status: C
The module provides students with an opportunity to consider, reflect on and develop key skills that will provide the basis from successful study on the course. It provides an opportunity to consider personal strengths and learning styles, and to develop strategies to obtain maximum benefit from these.
Year: 1
Status: C
Crime and deviance are rarely out of the news with frequent media warnings, for example of rises in `anti-social behaviour'. This module encourages students to look beneath the headlines and examine social constructions of crime. Ideas about `crime' and `deviance' vary over time and place and the module explores popular discourses on these themes. Methods of measuring crime are critically assessed and the fear of crime is explored. The module introduces students to criminology as a discipline and to key theoretical traditions. Students are supported in developing the critical skills needed to evaluate competing perspectives. The module provides a foundation of knowledge and skills for the criminology and criminal justice, and criminology minor degree programmes.
Year: 1
Status: C
This module will explore crime and its control through an analysis of specific crime problems and the response of the criminal justice system to these problems, drawing upon an array of national and international research evidence, and current developments. Students will be introduced to major offending patterns in Northern Ireland and the United Kingdom. Consideration will also be given to the agencies, and policy frameworks, around which crime control is organised.
Year: 1
Status: C
This module provides an overview of recent developments in criminological explanations of crime and criminalisation. These developments are explored and critically evaluated via contemporary issues such as gender & crime, cyber psychology, community safety & social control, and race that face today's society.
Year: 2
Status: C
This module seeks to explore the definition and nature of state crime in criminological and political discourse. It aims to develop a critical understanding of the nature of the state and the scale and type of crimes committed by state agents and agencies. A range of state crimes will be explored in both the domestic and international spheres. The module will explore forms of state crime as techniques of 'coercive governance' and will use examples from both democratic and authoritarian regimes.
Year: 2
Status: C
The research methods module has a direct link to the students' preparation for their undergraduate dissertations. The module considers the key research strategies and designs in the field of criminology and criminal justice and then examines various quantitative and qualitative research methods. Central to the module is practical skills acquisition using data analysis software packages to interrogate primary and secondary data in the social sciences. The module concludes with an examination of ethical issues which must be considered in advance of embarking on primary research in the dissertation.
Year: 2
Status: C
This module examines the relationship between sentencing theory, principle, policy, and practice. Consideration is given to how sentences are constructed, and the range of sentencing technologies available to the courts. Additionally, a variety of theoretical approaches are utilised to explore the broader social impact sentencing and punishment has on communities at a regional, national, and international level.
Year: 2
Status: C
This module explores the characteristics, dynamics and underpinning factors that exist between policing and society. Historically, policing has been the subject of much debate both nationally and internationally, with the delivery of policing services, and, how they are perceived by the community focal points for discussion. Through the policing institutions in Northern Ireland and England and Wales this module will examine how various social, cultural and political forces impact upon the police and the community they serve. It is also important to consider the role of the community in the context of `policing' and examine the various techniques employed by civil society to address issues pertaining to community safety and the fear of crime. The module will also consider the emergence of new crimes in the form of `internet and organised crime' and determine the implications on the relationship between society and the police.
Year: 2
Status: C
This module provides an overview of the history and development of the modern youth justice system in GB and NI. It explores sociological and criminological concepts relating to 'childhood' 'adolescence' and 'juvenile delinquency'. The module explores crime committed by young people, its causes, consequences and treatment and the victimisation of young people. It critically analyses current debates and issues regarding youth crime and youth justice within a children's rights framework.
Year: 2
Status: C
The field of criminal justice is a dynamic, evolving and expanding landscape. It is therefore extremely important for students who are to become future policy experts and practitioners to engage with this landscape reflectively and critically. To do this, future criminal justice experts must be equipped with a range of technical skills and tools of critical analysis that are used to evaluate the functioning and effectiveness of criminal justice systems, and the diversity of services they deliver. This means that in addition to learning about the relationship between a theory and policy and practice, students must be able to offer an informed critique of it. It is through these processes that practitioners can develop practice models and improve the services they provide. This module aims to support students' employability through applied criminology learning based on enquiry. They will learn how to apply the knowledge of criminological theory and policy to evaluate real world problems relating to crime and criminal justice; produce informed critiques of practice and policy; and develop solutions informed by theory. On this module, participants will development technical and critical analysis skills essential to the endeavour of applied criminology.
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
This module is designed to explore the law and institutions involved in policing and to set policing in a legal context. Thus it will consider the role and powers of the office of constable and the legal framework within which a policing service is delivered including the constraints and obligations on police officers and a police service. It will allow for discussion and challenge in regard to ideas about how policing is and ought to be conducted.
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
This course is about how, and why, a regime becomes either a democracy or a dictatorship. Can democracy survive in an agrarian society or a 'divided' society? Was Barrington-Moore correct when he made the observation 'no bourgeois, no democracy'? Is oil inevitably a curse (for democrats) and a blessing (for dictators)? How can a democratic government manage its 'praetorian problem': the risk of military coup? This course examines theories of regimes origin and survival in a range of case studies from across world regions.
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
This module provides students, who are new to restorative justice with an understanding of key theories. The module addresses principles of restorative practice. It also considers the community, policy and legal frameworks in which restorative justice may be located.
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
This module further develops analytical skills in criminology and criminal justice. It evaluates, in the national and international context, the experiences, and the actual and potential role of victims of crime within the criminal justice system and explores whether they should be afforded a greater role.
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
Crime and media explores the nature of media influence on crime, the criminal justice
system and the role that the media plays in influencing the public's perception of crime and
criminality. Specifically this module develops analytical and critical skills in exploring and
understanding the conflicting and at times ambiguous relationship between crime and the
media in the twenty first century.
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
This module is intended:
• To introduce students to the principles of environmental protection and governance.
• To engage students with critical debates from green criminology that challenge the conventional notions of crime, deviance and justice.
• To promote student awareness and understanding of issues relating to environmental harm and justice.
• To foster the development of applied knowledge of environmental protection, regulation and governance.
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
Since the late 1960s, acts of terrorism have become more numerous and wide-ranging. The attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon in September 2001 and the following incidents elsewhere, notably in Madrid and London, have given impetus to the study of terrorism and political violence, not in only in academic circles but also amongst policymakers. Furthermore, there is a more heightened awareness in the general public about the 'war against terrorism'. The module involves consideration of the debate over the definition of terrorism and political violence; psychological, sociological and other social science theories of terrorism and political violence; the symbiotic relationship between terrorists, terrorism and the mass media; the character of state terrorism; trans-national and international terrorism including past trends and future prospects and single-issue terrorism. The module also examines and assesses counter-terrorism (police, intelligence and legal) measures/responses by the state, both for their effectiveness and for their implications for civil liberty in liberal-democracies.
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
This module covers major debates, perspectives and challenges associated with children and families. It will consider policy and services for children's well-being and recent reviews of children's services including child protection services and key areas of provision. Students will examine perspectives on policy, child poverty, mixed economy of care, partnership and inter-agency work and children's participation and rights.
Status: O
Year: 3
This module is optional
This module provides an opportunity to undertake an extended period of study outside the UK. It is a required module for all criminology students on an intercalary study abroad year between second and final year. It is not open to non-study abroad students. Students will develop an enhanced understanding of the academic discipline of criminology and criminal justice whilst generating educational and cultural networks.
Status: O
Year: 3
This module is optional
This module provides undergraduate students with an opportunity to gain structured and professional work experience, in a work-based learning environment, as part of their planned programme of study. This experience allows students to develop, refine and reflect on their key personal and professional skills. The placement should significantly support the development of the student's employability skills, preparation for final year and enhance their employability journey.
Year: 4
Status: C
This module is designed to allow students to conduct an effective critical investigation of an area of concern or interest in the field of criminology and criminal justice, and to write a report on that investigation. Students will draw upon skills and knowledge acquired from taught modules and demonstrate their research skills acquired in the research methods module.
Year: 4
Status: C
The state has traditionally been viewed as being responsible for managing crime and policing in society. However, this is much more complex and varied than would initially seem obvious. This module will explore and evaluate public and community security from a number of perspectives, providing students with a wider appreciation of how policing is undertaken outside that of traditional state and police perspectives. This will involve an examination of the many configurations which contribute to broader conceptions of policing and security within modern society. Furthermore, the module will provide an understanding of the fact that the state police are but one of many auspices and agencies who contribute to the governance of security as part of common and diverse public demands for policing provision.
Year: 4
Status: C
This module includes an overview of the history of imprisonment as a form of punishment; the development of the prison system in the UK; discussion of key debates and current issues regarding imprisonment nationally and internationally. The module also covers the history, development of and current issues regarding imprisonment in Northern Ireland.
Year: 4
Status: C
Teaching is based on a mixture of short lectures, groupwork, and one-to-one advice from the teaching team. Former students will give presentations based on their experience of doing the dissertation at Ulster.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
'Lived experience and criminal justice' provides learners with the opportunity to undertake an innovative topic within the unique setting of the prison classroom. Students will acquire knowledge on the cutting-edge developments that integrate lived experience of criminal justice into programme delivery, policy reform, peer-led research and discipline advancements in the field of Convict Criminology. They will then work with inside students to apply this knowledge and learning to practical group project work-package development over the course of three weeks, which they will then present at their graduation ceremonies in week 12.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module explores and evaluates the legal framework within which surveillance operates in the United Kingdom. Considering the role of surveillance in society, the relationship between surveillance, privacy rights and fair trial rights is evaluated with specific reference to data protection, interception of communications, directed and intrusive surveillance, official secrecy, the security and intelligence services and recent developments in relation to identity and identity theft. Plus the role and impact of social media and the digital footprint we all leave behind.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
The purpose of this module is to provide students with an introductory grounding of the academic field of peace and conflict studies and the different approaches and interventions employed within it. Drawing on a range of international examples, students will gain an understanding of the various definitions and theoretical understandings of conflict, conflict transformation and peacebuilding and will develop a broad understanding of the various structural, economic, social and psychological impacts which require attention following violent conflict.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
Crime and media explores the nature of media influence on crime, the criminal justice system and the role that the media plays in influencing the public's perception of crime and criminality. Specifically this module develops analytical and critical skills in exploring and understanding the conflicting and at times ambiguous relationship between crime and the media in the twenty first century.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
Since the late 1960s, acts of terrorism have become more numerous and wide-ranging. The attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon in September 2001 and the following incidents elsewhere, notably in Madrid and London, have given impetus to the study of terrorism and political violence, not in only in academic circles but also amongst policy-makers. Furthermore, there is a more heightened awareness in the general public about the `war against terrorism'. The module involves consideration of the debate over the definition of terrorism and political violence; psychological, sociological and other social science theories of terrorism and political violence; the symbiotic relationship between terrorists, terrorism and the mass media; the character of state terrorism; trans-national and international terrorism including past trends and future prospects and single-issue terrorism. The module also examines and assesses counter-terrorism (police, intelligence and legal) measures/responses by the state, both for their effectiveness and for their implications for civil liberty in liberal-democracies.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
Crime and criminal justice as well as issues of law and order remain topical in contemporary society. This module will provide students a unique opportunity to investigate the workings of the criminal mind and what motivates an individual to commit crime. This module aims to introduce students to the principal theories and applications of psychology within the field of criminology. It enables students to develop a critical understanding of how psychological theory is applied to various criminological settings, which include youth crime; weapon carrying; arson and sexual crimes; psychopaths and serial killers, and criminal profiling.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module offers students the opportunity to study contemporary issues in criminology, with particular reference to green criminology, environmental crime and justice. It provides the opportunity to understand the nature of how crime is defined and considered outside of academia. It looks at real world issues and discusses the various, and at times, conflicting approaches undertaken by criminologists. Students are encouraged to critically evaluate criminological evidence and to make links with criminological theory and issues raised.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module will assist students to develop skills in understanding how different theories, concepts, methodological tools and data influence the ways in which we respond to gender and crime. The establishment of a more victim centred approach, and changes to offender management, will form the key elements of the module. Case studies will show how practitioners and policy makers are responding to the extensive reforms within the criminal justice and prison system.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
Increasing connectivity to the Internet has resulted in a growing amount of crime and deviance taking place in cyberspace. This cybercrime module examines a series of cyber enabled and cyber dependent crimes, the motivations of online offenders and how such crimes may be investigated and subsequently prevented. It examines the complex nature of cyber legislation in Europe and explores the difficulties of policing cyber activity on the surface and dark web. By the end of the module students will be able to evaluate the uncertainties, ambiguities and limits currently encountered in trying to regulate the Internet and digital technology.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module examines the various criminal dimensions of contemporary globalisation, their
global extent and significance and the roles they play in shaping the socio-economic
conditions and development trajectories of key global regions. It also considers various responses to global crime and evaluates their success as well as exploring the relationship between global crime and
popular culture. Students will understand issues relating to a) Spatial and temporal patterns of global crime; b) the link between different forms of organised crime and globalisation; and c) the key critiques of crime control measures.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module offers students the opportunity to study contemporary issues in criminology, with particular reference to drugs use; its consumption, regulation and criminalisation. It provides the opportunity to understand the nature of how drug use and crime are defined and considered inside and outside of academia. It looks at real world issues and discusses the various, and at times, conflicting approaches undertaken by criminologists. Students are encouraged to critically evaluate criminological evidence and to make links with criminological theory and issues raised.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
Rehabilitation and Desistance from Crime will introduce students to some of the key concepts and debates in the field of desistance studies. The module will encourage an appraisal of the relationships between rehabilitation, risk and resettlement in penal philosophy, policy and practice. Students will engage with debates on 'what works' in rehabilitative practice, and examine how desistance from crime can be supported, or stymied, by criminal justice processes.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
Corporate crime is a multi-trillion dollar global racket that represents a significant threat to markets, democracy, development, human rights and the environment. Crimes committed by corporations have been identified by the UK and US governments as one of the most pressing challenges for law makers today. This module will critically explore the drivers of corporate crime in a number of thematic areas including serious fraud, financial crime, corruption, environment, and human rights. Students will take a hands-on approach, investigating some of the most significant corporate crimes of the last two decades, using specially curated real-world materials such as indictments and deferred prosecution agreements. This case driven approach will open-up the inner workings of corporate crime and help students theorise some of the key drivers of illicit corporate activity. The module's applied focus will help prepare students for a potential career in the control of corporate crime, which is a fast growing and dynamic industry for criminology graduates.
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module introduces students to the sociology of migration, 'race' and ethnicity, with particular focus on the UK experience. It explores how international population movements and the global forces behind them continue to create the societies we have in the UK, Ireland and the EU today. The module examines the origins and development of racism, incorporating human rights perspectives to explore how it has shaped, and continues to shape the nature of society. We look at the role 'race thinking' has played in the production of inequalities and exclusions, as well as engage with contemporary debates and theoretical advances, particularly in relation to antiracism, whiteness, antisemitism, Islamophobia, citizenship and multiculturalism. The module specifically examines the debates in the local Northern Ireland context with reference to specific groups: ethnic minorities, Travellers, immigrants, refugees and asylum seekers.
We recognise a range of qualifications for admission to our courses. In addition to the specific entry conditions for this course you must also meet the University’s General Entrance Requirements.
The A Level requirement for this course is BBB*.
* Applicants can satisfy the requirement for the third A Level Grade by substituting a combination of alternative qualifications recognised by the University.
RQF Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Extended Diploma
Award profile of DDM.
You may also meet the course entry requirements with combinations of different qualifications to the same standard. Examples of qualifications include;
Smaller BTEC/OCR qualifications (i.e. Diploma or Extended Certificate / Introductory Diploma / Subsidiary Diploma) in combination with A Levels or other acceptable level 3 qualifications.
Note: BTEC Level 3 RQF Foundation Diploma, Diploma and Extended Diplomas in Children's Play, Learning and Development are not accepted.
BTEC Level 3 RQF National Extended Certificate in Children's Play, Learning and Development is accepted
To find out if the qualification you are applying with is a qualification we accept for entry, please check our Qualification Checker - our Equivalence Entry Checker.
We will also continue to accept QCF versions of these qualifications although grades asked for may differ. Check what grades you will be asked for by comparing the requirements above with the information under QCF in the Applied General and Tech Level Qualifications section of our Entry Requirements - View our Undergraduate Entry Requirements
120 UCAS Tariff points to include a minimum of five subjects (four of which must be at Higher Level) to include English at H6 if studied at Higher Level or 04 if studied at Ordinary level.
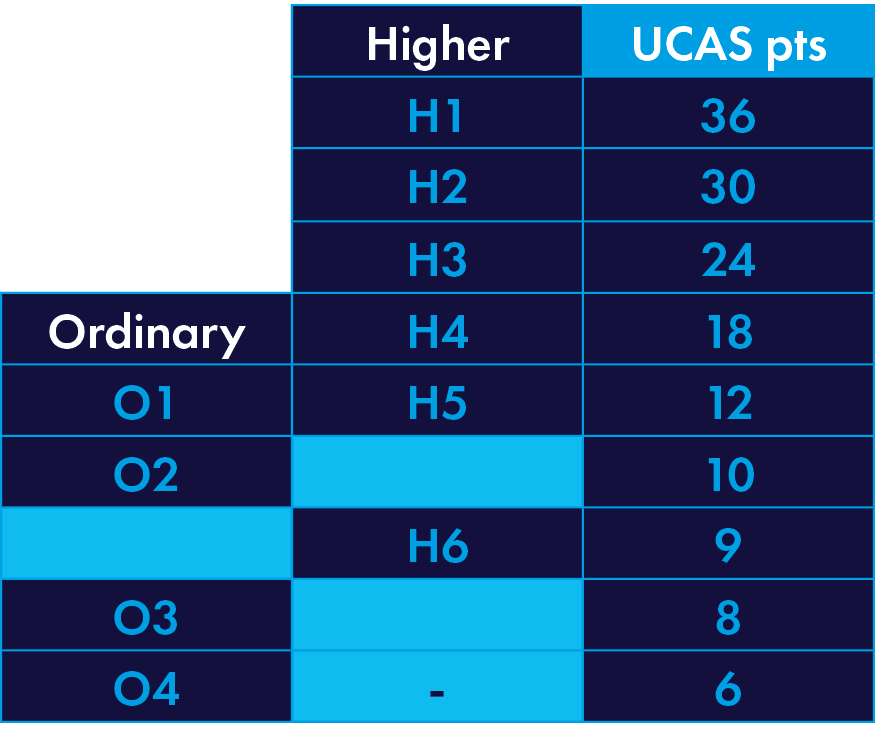
The Scottish Highers requirement for this course is grades BBBCC.
The Scottish Advanced Highers requirement for this course is grades CCC.
Overall International Baccalaureate profile minimum of 24 points (12 at higher level).
Grade 4 in Higher or Subsidiary Level English Language is also required.
Pass Access Diploma NI (120 credits) with an overall mark of 65%.
Pass Access to HE Diploma (GB) with 24 Distinctions and 21 Merits.
GCSE Profile to include CGSE English Language grade C/4 or above (or equivalent).
Level 2 Certificate in Essential Skills - Communication will be accepted as equivalent to GCSE English.
English language requirements for international applicants
The minimum requirement for this course is Academic IELTS 6.0 with no band score less than 5.5. Trinity ISE: Pass at level III also meets this requirement for Tier 4 visa purposes.
Ulster recognises a number of other English language tests and comparable IELTS equivalent scores.
You will enter Year 1. However, if you can provide evidence of previous relevant study, you may, in exceptional circumstances, be permitted exemption from a restricted number of modules in Year 1.
Graduates from this course are now working for:
With this degree you could become:
The course seeks to equip you for a variety of careers within organisations with a criminal justice or public policy focus, in the private, voluntary and statutory sectors. It also prepares you for a range of postgraduate opportunities in related fields.
Opportunities to study abroad include the Erasmus scheme and International Student Exchange Programme.
Whilst there is no formal work placement, there is a compulsory work based learning opportunity, entitled work volunteering and criminological issues for students who have secured two hours per week (or equivalent) volunteering or work experience for the duration of the 12 week module. The module aims to inform students about developments within current criminal justice policy and to encourage them to critically assess the role of their chosen organisation within this context and future employability.
Undergraduate fees are subject to annual review, 2026/27 fees will be announced in due course.
See our tuition fees page for the current fees for 2025/26 entry.
The Criminology and Criminal Justice degree has two awards sponsored by the Criminal Justice Inspection Northern Ireland:
Criminology and Criminal Justice students can also be considered for the School of Applied Social & Policy Sciences' Global Studies Award for the best dissertation with an international focus. Additionally, Criminology and Criminal Justice students are encouraged to submit their final year work to The Undergraduate Awards, an international awards programme which recognises creativity, excellence and innovative thinking within student coursework. We have had a number of entries which have been highly commended.
It is important to remember that costs associated with accommodation, travel (including car parking charges) and normal living will need to be covered in addition to tuition fees.
Where a course has additional mandatory expenses (in addition to tuition fees) we make every effort to highlight them above. We aim to provide students with the learning materials needed to support their studies. Our libraries are a valuable resource with an extensive collection of books and journals, as well as first-class facilities and IT equipment. Computer suites and free Wi-Fi are also available on each of the campuses.
There are additional fees for graduation ceremonies, examination resits and library fines.
Students choosing a period of paid work placement or study abroad as a part of their course should be aware that there may be additional travel and living costs, as well as tuition fees.
See the tuition fees on our student guide for most up to date costs.
Ulster continues to develop and support sustainability initiatives with our staff, students, and external partners across various aspects of teaching, research, professional services operations, and governance.
At Ulster every person, course, research project, and professional service area on every campus either does or can contribute in some way towards the global sustainability and climate change agenda.
We are guided by both our University Strategy People, Place and Partnerships: Delivering Sustainable Futures for All and the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Our work in this area is already being recognised globally. Most recently by the 2024 Times Higher Education Impact rating where we were recognised as Joint 5th Globally for Outreach Activities and Joint Top 20 Globally for Sustainable Development Goal 17: Partnership for the Goals.
Visit our Sustainability at Ulster destination to learn more about how the University strategy and the activities of Ulster University support each of the Sustainable Development Goals.
"It is very evident that staff work closely together as part of a very strong team and strive to help the students in any way possible".
"When need help it is provided efficiently. Tutors and lecturers are all approachable".
"Brilliant teachers. Interesting topics".
1. We prepare our prospectus and online information about our courses with care and every effort is made to ensure that the information is accurate. The printed version of the prospectus is, however, published at least a year before the courses begin. Information included in the prospectus may, therefore, change. This includes, but is not limited to changes to the terms, content, delivery, location, method of assessments or lengths of the courses described. Not all circumstances are foreseeable, but changes will normally be made for one of the following reasons:
2. If there are insufficient enrolments to make a course viable, it may be necessary for the University to withdraw a course. If you have received an offer for a course that we subsequently have to close, we will contact you as soon as possible to discuss alternative courses. If you do not wish to study any alternative courses at the University, you may withdraw your application by informing us by email to admissions@ulster.ac.uk.
3. Please note that the University’s website is the most up-to-date source of information regarding courses, campuses and facilities and we strongly recommend that you always visit the website before making any commitments.
4. We will include a durable PDF when we send you an offer letter which will highlight any changes made to our prospectus or online information about our courses. You should read this carefully and ensure you fully understand what you are agreeing to before accepting a place on one of our courses.
5. The University will always try to deliver the course as described in the durable PDF you receive with your offer letter.
6. At any point after an offer has been made, students will be notified of any course changes in writing (usually by email) as soon as reasonably practicable and we will take all reasonable steps to minimise their impact where possible. The University will, where possible and reasonably practicable, seek the express consent of the student in regard to any changes concerning material or pre-contract information.
7. The University website will be updated to reflect the changed course information as soon as reasonably practicable.
8. If, after due consideration, you decide that you no longer want to study your course or to study at the University because of the changes, you may withdraw your application or terminate your contract with the University. In order to do so, you should notify us in writing by emailing admissions@ulster.ac.uk (and update UCAS if applicable). We will, on request, recommend alternative courses that you could study with us, or suggest a suitable course at an alternative higher education provider.
9. If you do not agree that the changes are fair, you can seek redress under the Student Complaints Procedures.
10. Providing the University has complied with the requirements of all applicable consumer protection laws, the University does not accept responsibility for the consequences of any modification, relocation or cancellation of any course, or part of a course, offered by the University. The University will give due and proper consideration to the effects thereof on individual students and take the steps necessary to minimise the impact of such effects on those affected.
11. The University is not liable for disruption to its provision of educational or other services caused by circumstances beyond its reasonable control providing it takes all reasonable steps to minimise the resultant disruption to such services.
12. Further information can be found in our terms and conditions.
The full Student Terms and Conditions is now available.