Overview
How language works, is learned and used.
Summary
Are you the kind of person who notices things about language? Do you like words? Do you notice different people’s use of language, their accents, their word choices, maybe even their grammar? Did you like talking about grammar in school? If so, then linguistics is for you.
Here are some of the questions that linguists ask:
Why are there so many different languages? What do they have in common? How do children acquire language? What happens when we have problems using language, for example after a stroke? What is meaning and where do we get it from? How do we produce and comprehend sentences? What are the cultural, social and ideological processes that underlie the way we use language?
If you want to find out more about these questions, apply for Language and Linguistics.
We’d love to hear from you!
We know that choosing to study at university is a big decision, and you may not always be able to find the information you need online.
Please contact Ulster University with any queries or questions you might have about:
- Course specific information
- Fees and Finance
- Admissions
For any queries regarding getting help with your application, please select Admissions in the drop down below.
For queries related to course content, including modules and placements, please select Course specific information.
We look forward to hearing from you.
About this course
About
The Language and Linguistics course aims to give students foundational knowledge of the areas of linguistic theory and its applications. These areas include phonetics, morphology, syntax, semantics, pragmatics, historical linguistics, language acquisitionand discourse analysis. Primary teaching methods involve a mix of lectures and seminars both of which are heavily centred around working with examples of language data. In addition, a central element of a linguistics programme is the experience of independently collecting and analysing data and we aim to develop this skill in our students from the very first semester of the degree. Independent study and reading is also essential and the necessary study skills for independent study are developed over the three years of the degree. Assessment is by a mixture of data analysis exercises, essay based assignments, data centred research projects and formal examinations. The teaching team is made up of international, research-active linguists, educated in major Universities of Europe and the US.
We have designed our course to give you the flexibility to undertake a pathway which best suits your needs, so Language & Linguistics can be studied in conjunction with Counselling Studies. This allows you to combine your interest in language with the study of a vocational area in which effective use of language is central.
In second year, you can study abroad for a semester, for example in Switzerland, Germany or the US.
The programme offers students the opportunity to take up placements both locally and internationally in which their linguistics skills are applied in a range of English language teaching contexts.
The course lasts three years full-time. This course is also available by part-time study that can take a total of five years part-time.
Language and linguistics is a very mixed discipline. It is technical and analytical; it also requires personal reflection and observation, combined with a challenging attitude. The most important attribute that a candidate can have is a genuine and passionate interest in language and language use.
Associate awards
Diploma in Professional Practice International DPPI
Diploma in International Academic Studies DIAS
Attendance
Each module usually involves two hours of lectures plus a one hour seminar each week. In addition, students are required to undertake substantial directed independent learning.
Start dates
Teaching, Learning and Assessment
Students are taught primarily in blocks of two-hour lectures, plus one week of seminar per week. With three modules per semester, this means that the students would be in University for three days a week.
Assessement of the course is done through a variety of ways: coursework (individual and group), presentations, weekly assignments but also examinations.
Teaching, learning and assessment
The content for each course is summarised on the relevant course page, along with an overview of the modules that make up the course.
Each course is approved by the University and meets the expectations of:
Attendance and Independent Study
As part of your course induction, you will be provided with details of the organisation and management of the course, including attendance and assessment requirements - usually in the form of a timetable. For full-time courses, the precise timetable for each semester is not confirmed until close to the start date and may be subject to some change in the early weeks as all courses settle into their planned patterns. For part-time courses which require attendance on particular days and times, an expectation of the days and periods of attendance will be included in the letter of offer. A course handbook is also made available.
Courses comprise modules for which the notional effort involved is indicated by its credit rating. Each credit point represents 10 hours of student effort. Undergraduate courses typically contain 10, 20, or 40 credit modules (more usually 20) and postgraduate courses typically 15 or 30 credit modules.
The normal study load expectation for an undergraduate full-time course of study in the standard academic year is 120 credit points. This amounts to around 36-42 hours of expected teaching and learning per week, inclusive of attendance requirements for lectures, seminars, tutorials, practical work, fieldwork or other scheduled classes, private study, and assessment. Teaching and learning activities will be in-person and/or online depending on the nature of the course. Part-time study load is the same as full-time pro-rata, with each credit point representing 10 hours of student effort.
Postgraduate Master’s courses typically comprise 180 credits, taken in three semesters when studied full-time. A Postgraduate Certificate (PGCert) comprises 60 credits and can usually be completed on a part-time basis in one year. A 120-credit Postgraduate Diploma (PGDip) can usually be completed on a part-time basis in two years.
Class contact times vary by course and type of module. Typically, for a module predominantly delivered through lectures you can expect at least 3 contact hours per week (lectures/seminars/tutorials). Laboratory classes often require a greater intensity of attendance in blocks. Some modules may combine lecture and laboratory. The precise model will depend on the course you apply for and may be subject to change from year to year for quality or enhancement reasons. Prospective students will be consulted about any significant changes.
Assessment
Assessment methods vary and are defined explicitly in each module. Assessment can be a combination of examination and coursework but may also be only one of these methods. Assessment is designed to assess your achievement of the module’s stated learning outcomes. You can expect to receive timely feedback on all coursework assessments. This feedback may be issued individually and/or issued to the group and you will be encouraged to act on this feedback for your own development.
Coursework can take many forms, for example: essay, report, seminar paper, test, presentation, dissertation, design, artefacts, portfolio, journal, group work. The precise form and combination of assessment will depend on the course you apply for and the module. Details will be made available in advance through induction, the course handbook, the module specification, the assessment timetable and the assessment brief. The details are subject to change from year to year for quality or enhancement reasons. You will be consulted about any significant changes.
Normally, a module will have 4 learning outcomes, and no more than 2 items of assessment. An item of assessment can comprise more than one task. The notional workload and the equivalence across types of assessment is standardised. The module pass mark for undergraduate courses is 40%. The module pass mark for postgraduate courses is 50%.
Calculation of the Final Award
The class of Honours awarded in Bachelor’s degrees is usually determined by calculation of an aggregate mark based on performance across the modules at Levels 5 and 6, (which correspond to the second and third year of full-time attendance).
Level 6 modules contribute 70% of the aggregate mark and Level 5 contributes 30% to the calculation of the class of the award. Classification of integrated Master’s degrees with Honours include a Level 7 component. The calculation in this case is: 50% Level 7, 30% Level 6, 20% Level 5. At least half the Level 5 modules must be studied at the University for Level 5 to be included in the calculation of the class.
All other qualifications have an overall grade determined by results in modules from the final level of study. In Master’s degrees of more than 200 credit points the final 120 points usually determine the overall grading.
Figures correct for academic year 2022-2023.
Academic profile
The University employs over 1,000 suitably qualified and experienced academic staff - 60% have PhDs in their subject field and many have professional body recognition.
Courses are taught by staff who are Professors (19%), Readers, Senior Lecturers (22%) or Lecturers (57%).
We require most academic staff to be qualified to teach in higher education: 82% hold either Postgraduate Certificates in Higher Education Practice or higher. Most academic and learning support staff (85%) are recognised as fellows of the Higher Education Academy (HEA) by Advance HE - the university sector professional body for teaching and learning. Many academic and technical staff hold other professional body designations related to their subject or scholarly practice.
The profiles of many academic staff can be found on the University’s departmental websites and give a detailed insight into the range of staffing and expertise. The precise staffing for a course will depend on the department(s) involved and the availability and management of staff. This is subject to change annually and is confirmed in the timetable issued at the start of the course.
Occasionally, teaching may be supplemented by suitably qualified part-time staff (usually qualified researchers) and specialist guest lecturers. In these cases, all staff are inducted, mostly through our staff development programme ‘First Steps to Teaching’. In some cases, usually for provision in one of our out-centres, Recognised University Teachers are involved, supported by the University in suitable professional development for teaching.
Figures correct for academic year 2022-2023.
Modules
Here is a guide to the subjects studied on this course.
Courses are continually reviewed to take advantage of new teaching approaches and developments in research, industry and the professions. Please be aware that modules may change for your year of entry. The exact modules available and their order may vary depending on course updates, staff availability, timetabling and student demand. Please contact the course team for the most up to date module list.
Year one
Communication and Language
Year: 1
Status: C
The module explores the complex relationship between language and communication, focusing on competing models of communication and the multi-layered multi-faceted nature of meaning in communication involving language. It explores how understanding features of language informs the study of communication and how reflecting on communication aids reflection on the complex nature of language and meaning.
Children's Language
Year: 1
Status: C
This module introduces students to the study of first language acquisition. It covers the major methods of studying children's language, outlines the typical course of language acquisition. It provides the students with hands on experience of second language acquistion.
Analysing Language I
Year: 1
Status: C
This module aims to give students a solid grounding in the analysis of spoken language. It provides an overview of the place of phonetics and phonology in the human linguistic capacity and covers the production and perception, anatomical and physiological bases of speech, as well as the basic knowledge and tools required for phonological analysis.
Analysing Language II
Year: 1
Status: C
The module provides a comprehensive and basic introduction the levels of morphology and syntax. It introduces specific methodologies of data analysis employed in the field of word and sentence structure. Students will learn to use descriptive tools in order to observe and describe grammatical phenomena in English and other languages.
How language works
Year: 1
Status: C
This module provides an introductory overview of the relevant aspects of language how they are approached within linguistics. The module therefore will provide students with an overview of their subject and their course and help them understand how the different subjects within linguistics fit together.
Varieties of English
Status: O
Year: 1
This module is optional
This module will survey dialectal variation in English as spoken in Ulster and further afield, sampling from variation in accent, vocabulary, sentence construction and meaning. The material will introduce students to core theoretical concepts underpinning the study of language as a structured system via relatable examples. Students will learn to draw descriptive linguistic generalisations through hands on data analysis.
Nature and Contexts of Counselling
Status: O
Year: 1
This module is optional
The module will introduce you to the nature and purposes of counselling as a professional activity. Issues of definition and context will be addressed along with broader issues relating to the contemporary status of the profession and the personal and professional challenges inherent in good practice. Through the study of counselling in action, it is anticipated that that you will become familiar with counselling theories/approaches and a range of professional, ethical, and legal issues. Additionally, you will also become aware of social justice and international perspectives on counselling.
Year two
Talk, Interaction and Social Organisation
Year: 2
Status: C
This module develops students' ability to make, defend and present their own inductively developed observations about the rules and structures of language use in context and the relationship between language use and social/institutional context.
Semantics
Year: 2
Status: C
This module provides a comprehensive introduction to semantics. Semantics is the study of meaning, from the contribution of words to their combination into sentences. Building on the descriptive understanding of meaning developed in Year 1, students will consider how sentence meanings are deployed by speakers in communication.
Linguistic Theory I
Year: 2
Status: C
One of the main aims of linguistics is to understand the limits of cross-linguistic variation. Linguistic typology is a method of discovering the nature of language, by focusing exactly on the variation among linguistic systems. Variation among linguistic systems is vast, but not unconstrained, and linguistic variation focuses exactly on what is possible, rather than what is impossible in human language. This module is designed to introduce students to cross-linguistic variation, and the field of linguistic typology, in addition to touching upon some phenomena to address in some more detail.
Language Acquisition
Year: 2
Status: C
This course introduces students to theoretical approaches to first and second language acquisition
Research Methods in Linguistics
Year: 2
Status: C
This module aims to facilitate the students' critical engagement with the research process by supporting them in reviewing the current theoretical literature and research methods for a topic of their choice in language and/or linguistics. This module supports the students' development as researchers by engaging students in methodological debates and by making explicit those approaches to data that are predominantly implicit.
Counselling Theory
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
This module will introduce students to the field of counselling, how it has developed as a profession and its components, including clinical assessment and case formulation. The module will focus on three approaches to counselling: person-centred therapy, psychodynamic therapy and cognitive-behavioural therapy. Students will read a range of clinical writings in the field of counselling, and discuss a number of case studies to link theory to practice.
Principles of Phonetics
Status: O
Year: 2
This module is optional
By studying this module students will engage with current analytic frameworks in acoustic and articulatory phonetics. The module contributes to the development of the student's analytical skills through the examination of phonetic data. Training in acoustic software will develop the students' technical skills and their application to data analysis.
Year three
Work Placement
Status: O
Year: 3
This module is optional
This module provides undergraduate students with an opportunity to gain structured and professional work experience, in a work-based learning environment, as part of their planned programme of study. This experience allows students to develop, refine and reflect on their key personal and professional skills. The placement option is a complement to and extension of the work engaged in at the University and provides the opportunity for each student to apply theory to practice, enhance their employability portfolio and improve their career planning skills and knowledge.
Year four
Dissertation
Year: 4
Status: C
The project enables students to apply methods and techniques to exending and applying their knowledge and understanding of Communication and allows them to further develop their conceptual, rational and creative thinking within the field of Communication. It incorporates all aspects of completing a research project, from topic selection through to writing up and builds upon research skills acquired in Years 1 and 2.
Researching Talk
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
Building on CMM320, this module engages students in detailed examination of the sequential organization of talk-in-interaction. They will develop a firm understanding of both the analytical constructs of Conversation Analysis and the ethnomethodological underpinnings that distinguish Conversation Analysis from other approaches to social interaction. Students will also put that understanding into practice through a supported research project.
Current Issues in Linguistics
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module introduces students to contemporary work in linguistic theory. Precise topics covered will vary with developments in the discipline, but will include work at the forefront of current research, enabling students to become acquainted with current work in the field and to develop a critical perspective on research in the area.
Language Acquisition
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module introduces students to contemporary work in language acquisition, both first language acquisition and second/foreign acquisition. Precise topics covered vary with developments in the discipline, but will include work at the forefront of current research, enabling students to become acquainted with current work and to develop a critical perspective on research in the area.
Critical Issues in Counselling Studies
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module provides students with an understanding of one of the major areas of applied communication. The module will enable students to gain an overview of the major theoretical and empirical literature in the area of counselling and psychotherapy. The wider issues relating to professional, legal and ethical matters will also be addressed. The module is assessed by coursework and examination.
Linguistic Interfaces
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module supports the students' abilities of knowledge transfer and application by engaging students in current debates of linguistic interface issues and how they might solve problems which have previously created challenges for non-integrated approaches in traditional framework of generative grammar.
Investigating Ellipsis
Status: O
Year: 4
This module is optional
This module studies "ellipsis", or abbreviated versions of utterances. To a first approximation, ellipsis is possible in the context of an "identical" previous utterance, but the precise conditions are difficult to pin down and span the full array of linguistic domains. The course will survey a range of elliptical phenomena, with students evaluating the ability of various theoretical approaches to account for them.
Standard entry conditions
We recognise a range of qualifications for admission to our courses. In addition to the specific entry conditions for this course you must also meet the University’s General Entrance Requirements.
A level
BCC*
* Applicants can satisfy the requirement for an A-Level Grade C by substituting a combination of alternative qualifications recognised by the University.
Applied General Qualifications
RQF Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Extended Diploma / OCR Cambridge Technical Level 3 Extended Diploma
Award profile of DMM
We will also accept smaller BTEC/OCR qualifications (i.e. Diploma or Extended Certificate / Introductory Diploma / Subsidiary Diploma) in combination with A Levels or other acceptable level 3 qualifications.
To find out if the qualification you are applying with is a qualification we accept for entry, please check our Qualification Checker - https://www.ulster.ac.uk/study/entrance-requirements/equivalence
We will also continue to accept QCF versions of these qualifications although grades asked for may differ. Check what grades you will be asked for by comparing the requirements above with the information under QCF in the Applied General and Tech Level Qualifications section of our Entry Requirements - https://www.ulster.ac.uk/study/entrance-requirements/undergraduate-entry-requirements
Irish Leaving Certificate
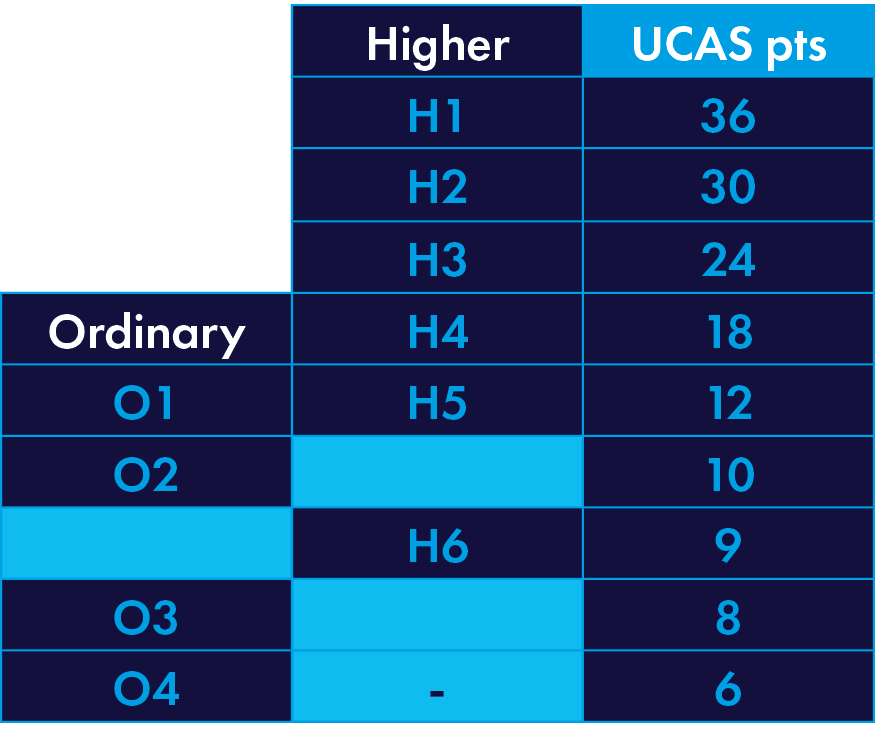
104 UCAS tariff points to include a minimum of five subjects (four of which must be at Higher Level) to include English at H6 if studied at Higher Level or O4 if studied at Ordinary Level.
Irish Leaving Certificate UCAS Equivalency
Tariff point chart
Scottish Highers
Grades BCCCC.
Scottish Advanced Highers
Grades CDD.
International Baccalaureate
Overall profile is minimum 24 points (including 12 at higher level).
Access to Higher Education (HE)
Overall profile of 60% (120 credit Access Course) (NI Access Course).
Overall profile of 12 credits at Distinction, 30 credits at Merit and 3 credits at Pass (60 credit Access Course) (GB Access Course).
GCSE
For full-time study, you must satisfy the General Entrance Requirements for admission to a first degree course and hold a GCSE pass at Grade C/4 or above in English Language (or equivalent). Level 2 Certificate in Essential Skills Communication will be accepted as equivalent to GCSE English.
English Language Requirements
English language requirements for international applicants
The minimum requirement for this course is Academic IELTS 6.0 with no band score less than 5.5. Trinity ISE: Pass at level III also meets this requirement for Tier 4 visa purposes.
Ulster recognises a number of other English language tests and comparable IELTS equivalent scores.
Additional Entry Requirements
Pass HND with overall Merit to include 30 distinctions in level 5 credits.
Pass HNC with overall Merit to include 60 distinctions in level 4 credits.
Successful completion of any Ulster University Foundation Degree with an average of 45% in Level 5 modules. (Entry into Year One only)
You may also meet the course entry requirements with combinations of different qualifications to the same standard as recognised by the University.
Exemptions and transferability
Language and Linguistics is available as a single subject degree or with a optional exit pathway in Counselling studies (upon completion of three modules).
Careers & opportunities
Career options
When you choose a Language and Linguistics degree, you are keeping your career options very open. It is very relevant to any job where you need to communicate effectively using language (which is most jobs!) and as a linguistics student, you will experience a mixture of arts based thinking, social science research skills and scientific analysis skills that give you a much broader range of transferable skills than the average graduate.
A Language and Linguistics degree is also more specifically relevant if you are interested in a career in Speech Therapy; Audiology; Teaching; Teaching English as a Second Language; Publishing; Law or Professional Communication. It is also a subject which will provide you with an impressive range of transferable skills highly relevant to the workplace.
Our website includes some graduate profiles so you can read why some of our students chose this programme and how they got from the degree to their current profession.
Work placement / study abroad
The programme offers students the opportunity to take up placements both locally and internationally in which their linguistics skills are applied in a range of English language teaching contexts.
Fees and funding
Northern Ireland, Republic of Ireland and EU Settlement Status Fees
£4,750.00
England, Scotland, Wales and the Islands Fees
£9,250.00
International Fees
£16,320.00
Additional mandatory costs
It is important to remember that costs associated with accommodation, travel (including car parking charges) and normal living will need to be covered in addition to tuition fees.
Where a course has additional mandatory expenses (in addition to tuition fees) we make every effort to highlight them above. We aim to provide students with the learning materials needed to support their studies. Our libraries are a valuable resource with an extensive collection of books and journals, as well as first-class facilities and IT equipment. Computer suites and free Wi-Fi are also available on each of the campuses.
There are additional fees for graduation ceremonies, examination resits and library fines.
Students choosing a period of paid work placement or study abroad as a part of their course should be aware that there may be additional travel and living costs, as well as tuition fees.
See the tuition fees on our student guide for most up to date costs.
Disclaimer
- Although reasonable steps are taken to provide the programmes and services described, the University cannot guarantee the provision of any course or facility and the University may make variations to the contents or methods of delivery of courses, discontinue, merge or combine courses and introduce new courses if such action is reasonably considered to be necessary by the University. Such circumstances include (but are not limited to) industrial action, lack of demand, departure of key staff, changes in legislation or government policy including changes, if any, resulting from the UK departing the European Union, withdrawal or reduction of funding or other circumstances beyond the University’s reasonable control.
- If the University discontinues any courses, it will use its best endeavours to provide a suitable alternative course. In addition, courses may change during the course of study and in such circumstances the University will normally undertake a consultation process prior to any such changes being introduced and seek to ensure that no student is unreasonably prejudiced as a consequence of any such change.
- The University does not accept responsibility (other than through the negligence of the University, its staff or agents), for the consequences of any modification or cancellation of any course, or part of a course, offered by the University but will take into consideration the effects on individual students and seek to minimise the impact of such effects where reasonably practicable.
- The University cannot accept any liability for disruption to its provision of educational or other services caused by circumstances beyond its control, but the University will take all reasonable steps to minimise the resultant disruption to such services.
Testimonials
Our students say:
“I enjoyed every one of the three years because they were so varied, whether we were interviewing people on campus; recording our families and analysing their communication or learning about the sounds that make up the languages of the world.”
“I found the course useful in helping me to understand more about communication: from how language is acquired and speech produced to how social processes affect and are affected by language.”
“My degree in language and linguistics has proved to be a solid base for my current job; it gave me sound preparation in terms of knowledge for the TEFL CERT and was favourably looked on by employers too. I would recommend for it for the various opportunities and career paths it presents upon completion of the course.”
“I firmly believe that the BSc Hons Language and Linguistics has given me the skills required to become an adaptable and effective manager in many capacities.”
“I have no doubt that the Language and Linguistics course has helped me get to where I am today and I would absolutely recommend the course to anyone who is considering it.”
“I enjoyed doing a challenging degree that was something very different from what my friends were doing. Finishing it gave me a great sense of achievement.”
“Language and linguistics gave me a lot of skills for my employment: from practical skills like doing presentations and writing, to more transferrable skills like analytical and critical thinking.”
“Language and linguistics lecturers are very enthusiastic for their discipline and are very approachable.”